What is influenza virus
Influenza viruses are members of the family Orthomyxoviridae. It contains a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA genome.
Properties of influenza virus:
- Five genera: Influenzavirus A, Influenzavirus B, Influenzavirus C, Thogotovirus, and Isavirus
- Virions are pleomorphic, spherical, or filamentous, 80 to 120 nm in diameter
- Envelope peplomers consist of rod-shaped hemagglutinin (HA) homotrimers and mushroom-shaped neuraminidase (NA) homotetramers
- The envelope is lined by matrix protein (M1) on the inner surface and contains a small number of pores composed of protein M2
- The genome consists of linear negative-sense, single-stranded RNA, divided into eight (genera Influenzavirus A and Influenzavirus B), or seven (genus Influenzavirus C), or six (genus Influenzavirus C) segments, 10 to 13.6 kb in overall size
- Virions contain 8, 7, or 6 separate helical nucleocapsids corresponding to each gene; for influenza A and B, each contains nucleoprotein (NP) and RNA polymerase complex (PA, PB1, PB2) in association with genome
- Transcription and RNA replication occur in the nucleus; capped 5′-termini of cellular RNAs are cannibalized as primers for mRNA transcription; budding takes place upon the plasma membrane
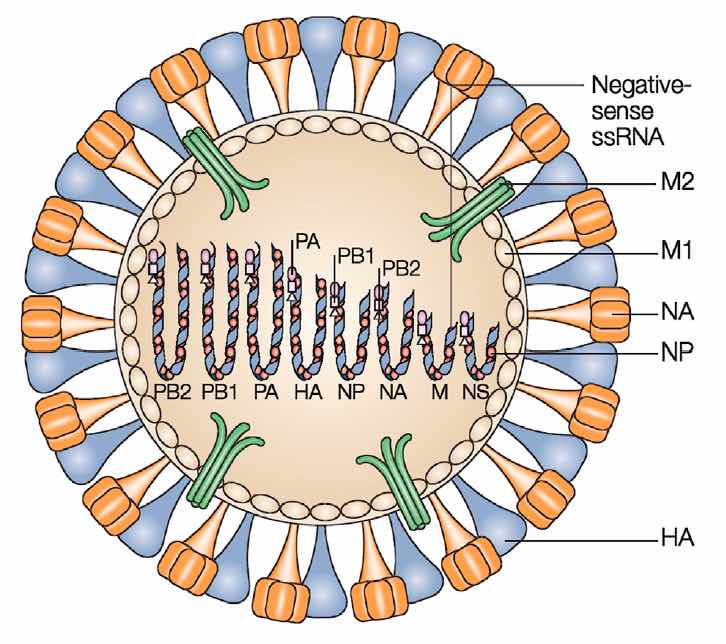
Figure 1.Diagram of influenza virus showing envelope and hemagglutinin (HA), neuraminidase (NA) and matrix (M2) projections, as well as the eight nucleocapsid segments (RNA and associated proteins) of influenza A viruses.
What’s the structure of influenza virus
The genome in eight, seven, or six segments consists of linear negative-sense single-stranded RNA, 10 to 13.6 kb in overall size. The genome segments have terminal repeats at both ends, those on the 3′-ends being identical on all segments.
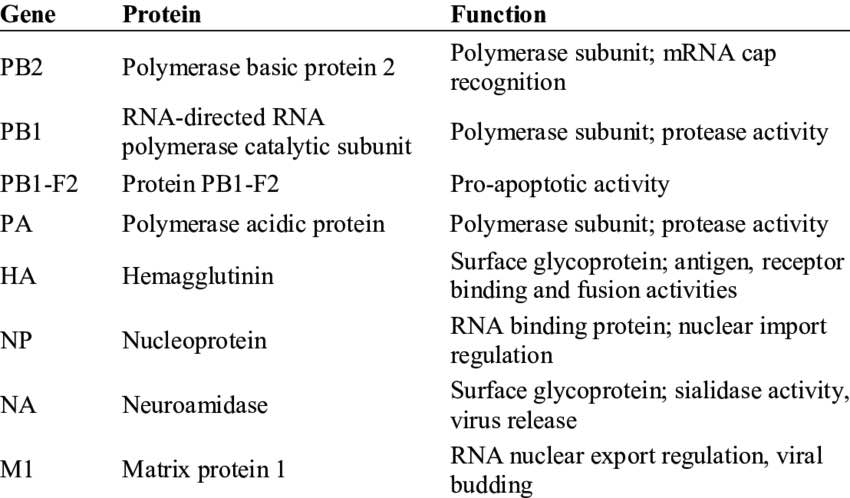
Figure 2.Proteins of the influenza A virus..
How does influenza virus replicate
Replication of RNA genome segments requires the synthesis of full-length positive-sense RNA intermediates, which unlike the corresponding mRNA transcripts, must lack 5′-caps and 3′-poly(A) tails.
Newly synthesized nucleoprotein binds to these full-length positive-sense RNA templates, facilitating the synthesis of nascent RNA genome segments. Late in infection, the matrix protein M1 enters the nucleus and binds to nascent RNA molecules, thereby down-regulating transcription and permitting export from the nucleus and subsequent assembly of nucleocapsids into virions.
Virions are formed by budding, incorporating M protein and nucleocapsids aligned below patches on the plasma membrane in which hemagglutinin and neuraminidase peplomers have already been inserted. As virions bud, the neuraminidase peplomers facilitate the “pinching-off” and release of virions by destroying receptors on the plasma membrane that would otherwise recapture virions and retain progeny virions at the cell surface.
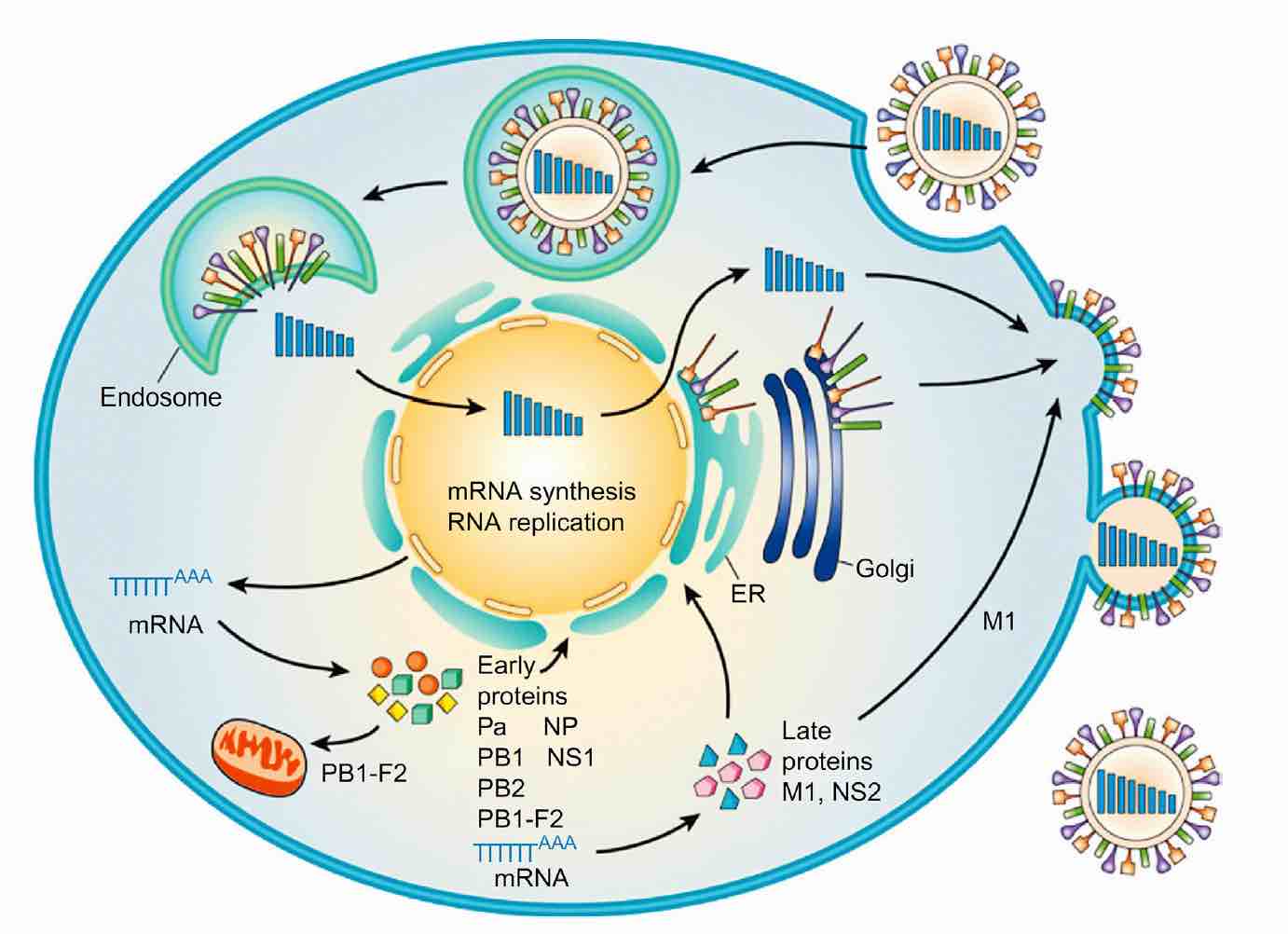
Figure 3.Replication cycle of influenza virus.
Reference:
Echo Biosystems is committed to delivering high-quality proteins to support your scientific research. We have developed a series of high-quality Influenza virus proteins including glycoprotein, Matrix protein, Nucleoprotein, and Phosphoprotein to meet your research needs.
- Product Name
- Organism
- Tag (Tag info)
- Expression Host (Source)
-
Recombinant Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein(NP)Influenza B virus (strain B/Lee/1940)N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein(NP)
-
Recombinant Influenza B virus Non-structural protein 1(NS)Influenza B virus (strain B/Lee/1940)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Influenza B virus Non-structural protein 1(NS)
-
Recombinant Influenza A virus Matrix protein 1(M)Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Iowa/1943 H1N1)N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Influenza A virus Matrix protein 1(M)
-
Recombinant Influenza A virus Matrix protein 2(M),partialInfluenza A virus (strain A/USA:Phila/1935 H1N1)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Influenza A virus Matrix protein 2(M),partial
-
Recombinant Influenza A virus Non-structural protein 1(NS)Influenza A virus (strain A/Hickox/1940 H1N1)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Influenza A virus Non-structural protein 1(NS)
-
Recombinant Influenza A virus Hemagglutinin(HA),partialInfluenza A virus (strain A/Hickox/1940 H1N1)N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Influenza A virus Hemagglutinin(HA),partial
-
Recombinant Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein(NP)Influenza B virus (strain B/Lee/1940)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedYeast
Recombinant Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein(NP)
-
Recombinant Influenza A virus Non-structural protein 1(NS)Influenza A virus (strain A/Hickox/1940 H1N1)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedYeast
Recombinant Influenza A virus Non-structural protein 1(NS)
-
Recombinant Influenza A virus Polymerase acidic protein(PA),partialInfluenza A virus (strain A/x-31 H3N2)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedE.coli
Recombinant Influenza A virus Polymerase acidic protein(PA),partial
-
Recombinant Influenza A virus Matrix protein 2(M)Influenza A virus (strain A/USA:Phila/1935 H1N1)N-terminal 6xHis-taggedin vitro E.coli expression system
Recombinant Influenza A virus Matrix protein 2(M)
